
If a neutral atom has 10 protons, it must have 10 electrons. If a neutral atom has 2 protons, it must have 2 electrons. If a neutral atom has 1 proton, it must have 1 electron. In other words, a neutral atom must have exactly one electron for every proton. This means that the negative charge on an electron perfectly balances the positive charge on the proton. Negative and positive charges of equal magnitude cancel each other out. Covalent bonding is also directional, meaning that the atoms only bond in specific directions giving the molecules definite shapes.\): Properties of Subatomic Particles Particle Double lines represent double bonding between the molecules (i.e atoms involving two electron pairs) and triple lines represent triple bonding. A single line between molecules indicates that there is a covalent bond between two atoms. Molecular Bonding: The atoms in a molecule are bonded together by an interatomic linkage that arises out of sharing of electrons. For example, a gold coin is simply a very large number of gold atoms molded into the shape of a coin, with small amounts of other, contaminating elements. This is why it is harder to melt solids than to boil liquids. An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains all of the chemical properties of an element. The higher the bond energy, the harder it becomes to separate the atoms. Radioactivity is the spontaneous release of energy from an unstable atom to. The energy of attraction or repulsion between atoms is called bond energy. The Ionized Atom Radioactive atoms have unstable blends of protons and neutrons. These are the forces of attraction and repulsion that make up the nuclear bond in the atom.
#ATOM DEFINITION FREE#
Molecules are formed to get stable and they exist in a free state.Įxcept for noble gases, all other atoms of elements possess certain levels of reactivity.Ītomic Bonding: The Coulombic forces exist between the nuclei and the electrons. Molecules do not exhibit the same properties as its constituting atoms.Ītoms may or may not be stable depending upon the number of electrons in its outermost or valence shell. The atoms of a molecule are held together by means of covalent bonds.Ītoms exhibit the same properties of its constituting element. The components of the atom are held together by means of nuclear bonds.

Molecules are made of atoms of the same or different elements. Atoms can combine with other atoms to form molecules but cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary chemical processes. Molecules are the basic unit of a compound.Ītoms are made up of Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. atom, the basic building block of all matter and chemistry. It is expressed in Atomic Mass Unit (amu). It is roughly equivalent to the mass of the total protons and neutrons in the nucleus as the mass of electrons is negligible. An example of an atom is a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom. Atomic Mass: It is the total mass of the atom in an element. An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the chemical properties of an element.Mass number: Mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of the atom. Illustrate a simple model of the nuclear atom locate its subatomic particles and their charges Explain why atoms have no overall charge Define ion and use.Atomic number: Atomic number is the total number of protons present in an atom.The number of protons in an atom of an element remains constant whereas the number of neutrons can change. Neutrons: Neutrons are neutral particles present inside the nucleus of the atom.The mass of the electrons is 1/1836 the mass of protons, thus making it negligible. The weighted average of the isotopic masses of an element, on a scale where an atom of carbon-12 has a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units.
#ATOM DEFINITION SERIES#
The electrons orbit around the nucleus in a series of levels called energy levels.

Protons: Protons are positively charged particles.
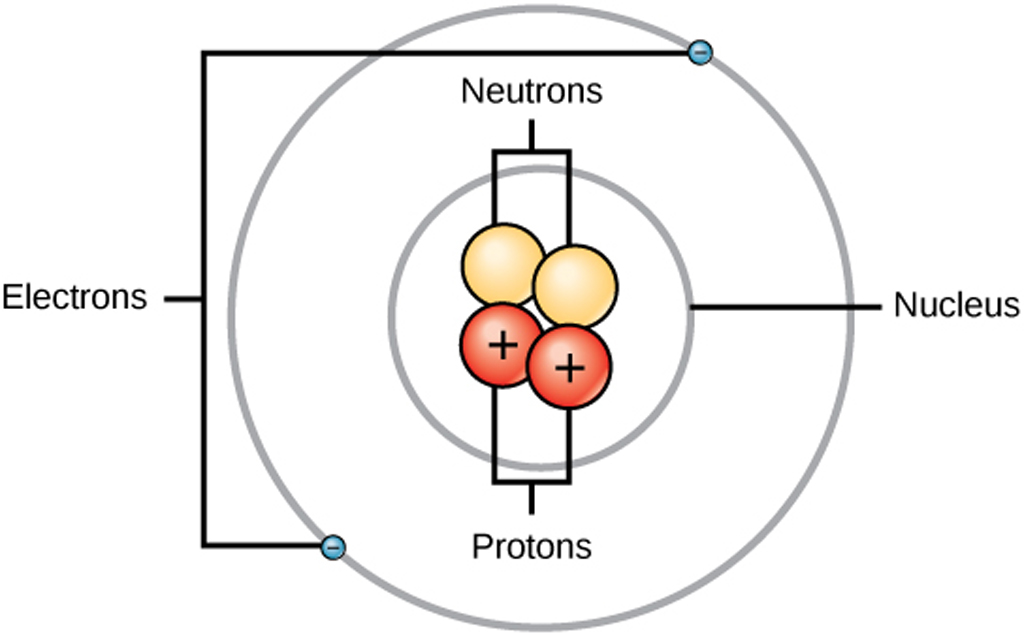
Some of the important terminologies are given below. The atoms are further subdivided into protons, electrons and neutrons. It is so minute in size that it cannot even be seen under a microscope. They exhibit properties relative to the element. Keyterms: Protons, Electrons, Neutrons, nucleons , nucleus, Microscope, Atomic mass, Atomic number, Mass numberĪtoms are the smallest unit of an element. Key Differences Between Atoms and Molecules.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
